
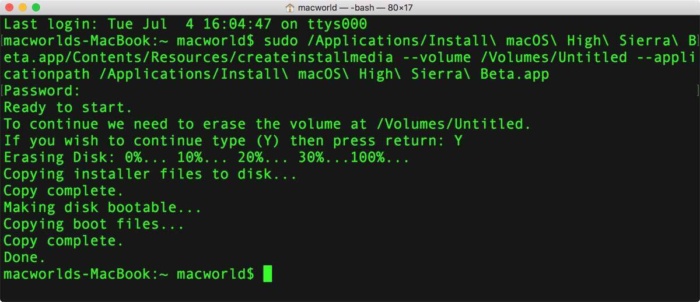
To navigate to the correct folder, we can use the cd command, as shown below. The next step is to navigate to the ZIP file and unzip it. `sudo yum install unzip` Step 3 – Unzip the ZIP File Using Terminal

Run your Node.js, Python, Go, PHP, Ruby, Java, and Scala apps, (or almost anything else if you use your own custom Dockerfiles), in three, easy steps! Ubuntu and Debianĭeploy your application to Kinsta. If you are managing a server that does not have the unzip package installed, you can use the following command to install it – note that sudo level permissions are required. Kinsta users do not have to worry about installing the unzip package because it is automatically installed on all our site containers. In some Linux distributions, the unzip package is not installed by default. Trying to restore a backup from a ZIP file? 🤐 Unzipping via SSH is your new secret weapon 🚀 Click to Tweet Step 2 – Install the Unzip Package (Optional) If you are not using public key authentication, you will also be prompted for the SSH password after executing the login command.Īfter a successful SSH login, you should see something like this in your Terminal window.

With the example login details below, the SSH terminal command would be ssh -p 24910. If you are using another web host or server provider, the SSH details can typically be found in your dashboard as well.Īfter you have found the login details, you can log in with the following SSH command. For Kinsta users, SSH login details along with the full SSH terminal command are provided in the MyKinsta dashboard. Now that we’ve covered the differences between password and public key authentication, let’s move on to the SSH login process.
If you are using another server provider, we recommend taking a look at the relevant documentation on how to upload SSH keys to the server. Kinsta users can upload SSH public keys in the MyKinsta dashboard. During the SSH login process, the cryptographic link between the two keys is verified to authenticate the user. The public key is uploaded to the server, while the private key is stored locally on your computer. The public key authentication method requires you to generate a key pair – public key and private key. Public key authentication is widely regarded as a more secure alternative to password authentication. The password authentication method uses a plain text password. When logging in to your server with SSH, there are two authentication methods – password and public key authentication. You may be wondering why the password is optional. To do this, you’ll need an SSH client like the built-in Terminal app in macOS and Linux or the free PuTTY client on Windows, and the SSH login details – IP address, username, password (optional), and port. The first step is to log in to your server with SSH.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
